Google is the core subsidiary of Alphabet Inc. and has expanded far beyond search to become one of the world’s largest technology ecosystems. Its work spans software, advertising, mobile platforms, cloud computing, hardware, and advanced
artificial intelligence. The company’s mission to organize information has evolved into building products and infrastructure that shape how billions of users interact with technology every day.
1. Google’s consumer and advertising product line remains its largest business segment. This includes Google Search, the world’s most widely used search engine; YouTube, a global leader in video content and digital advertising; and Android, the most widely adopted mobile operating system worldwide. Together, these platforms anchor Google’s advertising revenue and define its global reach.
2. Google’s enterprise and infrastructure product line supports businesses, developers, and organizations worldwide. This segment includes Google Cloud, which provides cloud computing, data analytics, and AI infrastructure; Google Workspace, the productivity suite that includes Gmail, Docs, Sheets, and Drive; and the company’s Pixel and Nest hardware lines, which integrate AI features across smartphones and smart home devices. It also includes Google Research and DeepMind, which advance foundational technologies used across the company’s broader product ecosystem.
3. Google’s AI product line is becoming increasingly central to its long-term strategy.
• Gemini 3.0, Google’s latest multimodal AI model used across Search, Workspace, and Android
• Gemini Advanced and Gemini for Enterprise, subscription AI services for individuals and organizations
• AI agents and developer tools that integrate with Google Cloud, Workspace, and mobile platforms
• DeepMind’s applied AI systems, which power optimization, safety research, and emerging agent capabilities
Although Google does not report AI as a standalone revenue category, AI drives a growing share of Cloud and product usage, and many new features across Google’s ecosystem are built directly on Gemini-based models.
Google vs. Nvidia vs. OpenAI: Who Is Winning the AI Race in 2025?
The AI race in 2025 is not defined by a single frontrunner but by three companies pushing the field forward from different angles. Google shapes how AI reaches billions of users,
Nvidia supplies the compute that trains most modern models, and OpenAI drives rapid progress in model development. Their roles intersect, yet each leads in a different part of the landscape.
Overall: Google’s Integrated Ecosystem Gives It a Strategic Advantage
Google’s strength in 2025 comes from a tightly connected AI stack. Google DeepMind builds the models, Alphabet operates TPU-powered data centers, and the company deploys AI across Search, YouTube, Android, Workspace, and Cloud. This alignment allows Google to update its entire ecosystem through a single model platform.
Nvidia leads AI compute with its GPUs but does not operate consumer-scale AI products. OpenAI moves quickly in model development but depends on external cloud and hardware. Microsoft drives enterprise AI through Azure yet lacks full control of the model stack and mobile distribution. Google remains the only company combining in-house model research, proprietary hardware, and immediate access to billions of users.
Model Comparison: Google Prioritizes Ecosystem Integration While AI Labs Compete Freely
Gemini 3.0 powers Google’s major products, from Search and Workspace to Android and Pixel. Instead of racing for benchmark wins, Google focuses on embedding Gemini into daily workflows, which gives the model broad, stable usage even if it is not the top performer in every test.
Other leading models in the AI competition
• Gemini 3.0 (Google) optimized for multimodal reasoning and integrated product experiences.
• Claude (Anthropic) strong in structured reasoning and safety-aligned enterprise tasks.
• Perplexity Model (Perplexity AI) designed for retrieval accuracy and search-style answers.
• DeepSeek V3.1 (DeepSeek Labs) effective in technical reasoning and certain trading simulations.
• GPT-5 Series (OpenAI) widely used through ChatGPT, APIs, and agent workflows.
• Grok-4 (xAI) built for real-time data access and fast iteration.
One interesting episode came from the Alpha Arena experiment on
Perp Dex Hyperliquid, where each model received ten thousand dollars to trade crypto perpetuals. After seventy-two hours, DeepSeek V3.1 and Grok-4 posted gains above fourteen percent, while GPT-5 and Gemini 2.5 Pro recorded losses. The results reflect performance within that specific setup and should not be viewed as a general ranking of model capability.
Despite intensive competition among model labs, Google’s strength remains its ability to deploy Gemini across products used daily by billions.
Hardware Comparison: Nvidia Leads Compute While Google Optimizes Internal Scale
Google trains and serves Gemini using Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), designed for efficient large-scale workloads across its own infrastructure. TPUs give Google control over cost and performance, though they are not widely used outside the company.
How hardware strategies differ
• Nvidia remains the industry leader in AI hardware, powering most global model training and inference.
• Google uses TPUs primarily within its own cloud and model pipeline, giving internal efficiency but limited market presence.
• OpenAI depends on Nvidia hardware through Microsoft Azure and does not operate its own chips.
Nvidia dominates the global compute layer, while Google focuses on running its internal AI stack efficiently.
Emerging Battlegrounds: Cloud Storage and Energy
As AI models scale, storage throughput and data movement have become major constraints. Google links TPU training systems directly with its storage layer, while AWS and Azure rely on global data networks to handle increasingly large datasets.
Decentralized storage platforms such as
Filecoin and
Arweave also provide distributed capacity for non-real-time data, adding another option to the storage stack.
Energy and cooling now determine how fast AI clusters can grow. Google is investing in renewable power, liquid-cooled TPU facilities, and exploring
nuclear-backed baseload sources to support long-term expansion. Nvidia continues improving GPU efficiency, while OpenAI relies on Microsoft’s growing data-center footprint, which also includes interest in nuclear-powered infrastructure. These factors increasingly shape the pace at which each company can scale next-generation AI systems.
How to Invest in Google Stocks: A Step-by-Step Guide in 3 Different Ways
Investors can gain exposure to Google through regulated stock markets or crypto-native products on BingX. Below are three clear paths depending on your preference for access, flexibility, or trading tools.
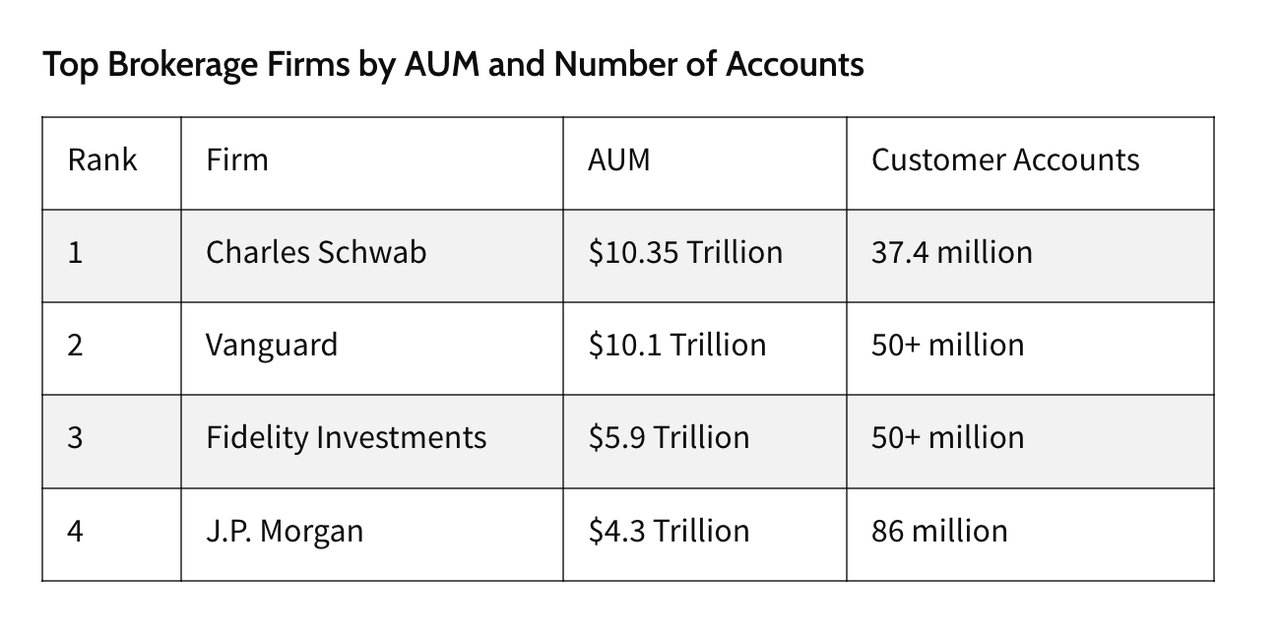
1. Buy Alphabet Shares (GOOGL / GOOG) on a Brokerage Platform