Filecoin Onchain Cloud's decentralized cloud infrastructure is designed to bring verifiable storage, programmable payments, and trustless data services on-chain. Built on the Filecoin network, it transforms traditional cloud storage into a fully auditable, cryptographically verifiable system where data, payments, and service guarantees are enforced by smart contracts.
Launching on mainnet in January 2026, Filecoin Onchain Cloud introduces a new paradigm for Web3 infrastructure, one where developers can build applications that own their data, automate payments, and verify service performance without relying on centralized cloud providers. As of early January,
Filecoin (FIL) is trading with a market cap of over $1.06 billion and a 7-day gain of over 17%, reflecting renewed market interest and growing momentum across the Filecoin ecosystem.
In this article, we explore how Filecoin Onchain Cloud works, why it matters for the future of decentralized infrastructure, and what the upcoming launch means for developers, enterprises, and investors alike.
What Is Filecoin (FIL) Decentralized Storage Network and How Does It Work?
Filecoin (FIL) is a
decentralized storage network that allows users to store, retrieve, and verify data on a global, permissionless marketplace. Instead of relying on centralized cloud providers, Filecoin connects users with independent storage providers who offer unused disk space in exchange for FIL tokens. The network uses cryptographic proofs, such as Proof of Replication and Proof of Spacetime, to ensure that data is stored securely and remains available over time.
FIL is the native utility token of the Filecoin network and is used to pay for storage, reward storage providers, and secure the network through economic incentives. Storage providers earn FIL for reliably storing data, while clients pay in FIL to upload and retrieve files. This market-driven model allows Filecoin to function as a decentralized, verifiable alternative to traditional cloud storage services.
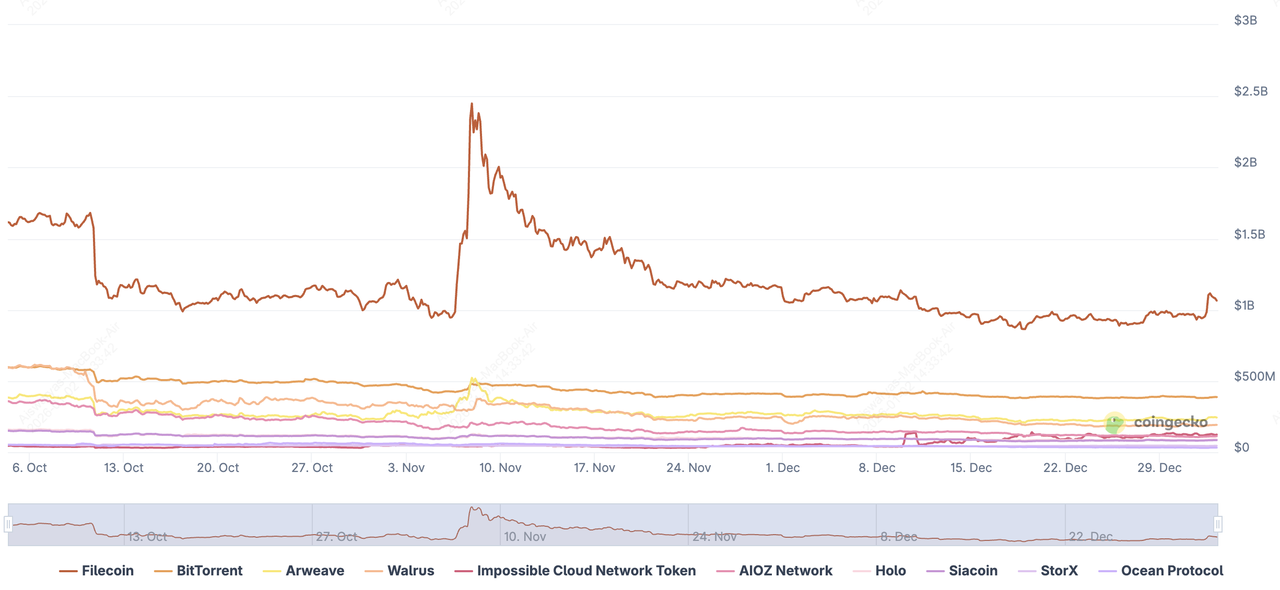
Filecoin dominates the decentralized storage token market | Source: CoinGecko
From a market perspective, Filecoin remains the dominant project in the decentralized storage sector, accounting for roughly 42% of the total storage market, which now exceeds $2.5 billion in value. As of the latest data, FIL trades around $1.44, with a 24-hour trading volume of over $266 million and a market capitalization of approximately $1.06 billion. The
FIL token is up 17% over the past week, reflecting growing investor interest as Filecoin expands its onchain cloud capabilities and strengthens its position as the leading infrastructure layer for decentralized data storage.
What Is Filecoin Onchain Cloud?
Filecoin Onchain Cloud is a programmable cloud platform that enables developers to deploy storage, retrieval, and payment logic directly on-chain. Unlike traditional cloud services such as AWS or Google Cloud, where trust is placed in a centralized provider, Filecoin Onchain Cloud uses cryptographic proofs and smart contracts to ensure that every operation is verifiable, auditable, and tamper-resistant.
At its core, Filecoin Onchain Cloud transforms Filecoin from a passive decentralized storage network into an active, on-chain cloud infrastructure. Storage providers, applications, and users interact through smart contracts that enforce service guarantees, payments, and data availability without intermediaries.
This architecture allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) that can:
• Store data verifiably
• Prove data availability in real time
• Automate payments for storage and retrieval
• Create programmable data-driven services
What Are the Real-World Use Cases of Filecoin's Onchain Decentralized Cloud?
Filecoin Onchain Cloud unlocks a wide range of decentralized applications, including:
1. Decentralized data storage and backups: Store critical data with cryptographic proof of availability.
2. AI and Machine Learning pipelines: Store and verify training datasets and model outputs.
3. Web3 applications and dApps: Host application data with on-chain verification and payments.
4. Decentralized data marketplaces: Monetize datasets with automated settlement and access control.
5. Enterprise compliance and archiving: Maintain immutable, verifiable records for audits and regulation.
How Does Filecoin Onchain Cloud Work?
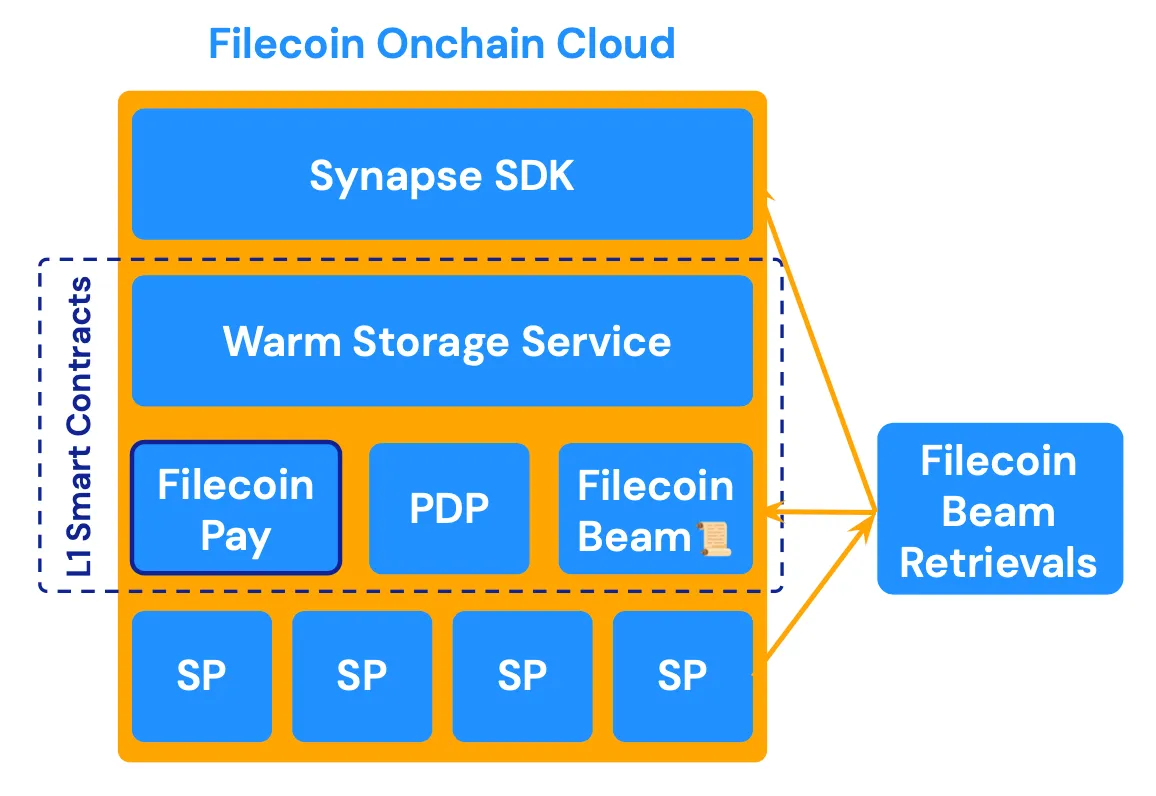
How Filecoin Onchain Cloud works | Source: Filecoin Cloud docs
Filecoin Onchain Cloud is built around modular, composable services that operate together as a unified system.
1. Filecoin Warm Storage (FWSS)
A verifiable storage layer designed for frequently accessed data. It provides:
• Fast data access
• Continuous proof of storage using cryptography
•
On-chain verification through Proof of Data Possession (PDP)
Unlike traditional cold storage, Warm Storage enables applications to retrieve data on demand while maintaining cryptographic guarantees that the data exists and remains intact.
2. Proof of Data Possession (PDP)
PDP is the cryptographic engine behind Filecoin Onchain Cloud. It continuously verifies that storage providers still possess user data without downloading it again. Each verification:
• Uses random cryptographic challenges
• Produces on-chain proofs
• Triggers automated payments or penalties
This ensures that data providers are only paid when they genuinely store the data.
3. Filecoin Pay for Onchain Payments
Filecoin Pay enables programmable, trustless payments tied directly to service performance. Payments are:
• Triggered by successful proof submissions
• Locked in smart contracts
• Released only when conditions are met
This eliminates disputes, middlemen, and delayed settlements common in traditional cloud billing.
4. Filecoin Beam Retrieval Layer
Filecoin Beam enables fast, low-latency data delivery from the network. It acts as a decentralized content delivery layer, ensuring files stored on Filecoin can be accessed quickly while remaining verifiable and censorship-resistant.
What Are the Key Features of Filecoin Onchain Cloud?
These core features define Filecoin Onchain Cloud and transforms its decentralized storage into a programmable, verifiable cloud infrastructure.
1. Verifiable Storage: Every byte stored is cryptographically proven to exist through Proof of Data Possession, ensuring trustless verification.
2. Programmable Infrastructure: Developers can define storage rules, payment logic, and data workflows directly in smart contracts.
3. Automated Payments: Payments occur automatically based on verified performance, removing the need for invoices, trust, or intermediaries.
4. Decentralized and Permissionless: Anyone can build, deploy, or participate, with no centralized gatekeepers.
5. Interoperable and Composable: Built on the Filecoin Virtual Machine (FVM), enabling integration with EVM-based tools, wallets, and smart contracts.
What Makes Filecoin Onchain Cloud Different From Traditional Cloud Services?
| Feature |
Traditional Cloud |
Filecoin Onchain Cloud |
| Data Ownership |
Provider-controlled |
User-owned |
| Trust Model |
Centralized trust |
Cryptographic verification |
| Payments |
Fixed, opaque billing |
On-chain, programmable |
| Transparency |
Limited |
Fully auditable |
| Vendor Lock-in |
High |
None |
| Availability Proof |
None |
On-chain verification |
Filecoin Onchain Cloud differs from traditional cloud services by replacing centralized trust with cryptographic verification. Instead of relying on a single provider to store, secure, and bill for data, Filecoin uses on-chain proofs, smart contracts, and decentralized storage providers to ensure data availability, integrity, and transparency at every stage.
Unlike traditional cloud platforms that operate behind closed systems, Filecoin Onchain Cloud enables programmable, auditable, and permissionless infrastructure. Data ownership remains with users, payments are executed automatically through on-chain logic, and service performance is verifiable in real time, eliminating vendor lock-in while creating a trust-minimized alternative to centralized cloud services.
Unlike Web2 cloud platforms, Filecoin Onchain Cloud ensures that data availability, payments, and service quality are provable on-chain, not just promised by providers.
When Does Filecoin Onchain Cloud Launch?
The Filecoin Onchain Cloud mainnet is scheduled to launch in January 2026, following successful testnet deployments and early developer adoption. Key milestones include:
• Late 2025: Public testnet and early partner integrations
• January 2026: Mainnet launch with Filecoin Warm Storage, Filecoin Pay, and Beam
• Post-launch: Expansion into advanced compute,
AI data pipelines, and enterprise-grade storage services
How to Trade Filecoin (FIL) on BingX
BingX makes it easy to trade Filecoin (FIL) using its AI-powered trading tools, offering both spot and futures markets for users who want to buy, sell, or trade FIL with flexibility and control.
How to Buy and Sell FIL on BingX Spot
FIL/USDT trading pair on the spot market powered by BingX AI insights
1. Log in to your BingX account and navigate to the
Spot trading section.
2. Search for the
FIL/USDT trading pair.
4. Your FIL will be credited instantly to your spot wallet after execution.
How to Trade FIL on BingX Futures
FIL/USDT perpetual contract on the futures market powered by BingX AI
2. Choose your preferred leverage and margin mode (cross or isolated).
3. Set your order type (market or limit), enter position size, and confirm the trade.
Final Thoughts: Why Filecoin Onchain Cloud Matters
Filecoin Onchain Cloud represents a major shift from trust-based cloud services to verifiable, onchain infrastructure. By embedding storage, payments, and verification directly into smart contracts, it enables developers to build transparent, censorship-resistant applications while giving enterprises greater confidence in data integrity and service accountability. This architecture moves decentralized storage from experimentation toward production-ready infrastructure.
As Filecoin Onchain Cloud approaches its January 2026 mainnet launch, it positions itself as a foundational layer for the next phase of Web3 infrastructure. However, like any emerging technology, adoption, network maturity, and long-term performance remain key factors to monitor as the ecosystem evolves.
Related Reading