Uniswap is one of the protocols that defined
decentralized finance (DeFi). It replaced traditional order books with automated liquidity pools, allowing anyone to trade ERC-20 tokens directly from their wallet. What began as a simple experiment in 2018 has grown into a multi-version protocol now used across
Ethereum and
Layer-2 networks.
Since its first release in 2018, Uniswap has rolled out four major upgrades, each introducing new mechanisms for pricing, liquidity, and capital efficiency. From V1’s basic AMM design to V4’s customizable hooks, every version marks a step forward in how decentralized finance has evolved and how developers continue to expand what on-chain markets can do.
What Is Uniswap?
Uniswap is a
decentralized exchange (DEX) protocol built on Ethereum that allows users to swap ERC-20 tokens without relying on centralized intermediaries. Founded in 2018 by Hayden Adams, the project was inspired by early discussions about automated market makers within the Ethereum community.
At a time when most token trading relied on order-book systems, Uniswap introduced a model based on permissionless liquidity pools governed by smart contracts. Its simple design made it easy for users and developers to create markets, add liquidity, and trade directly on-chain. Over time, Uniswap expanded beyond ETH swap on Ethereum and became a core piece of infrastructure across major
Layer-2 networks such as
Arbitrum,
Optimism,
Base, and
Polygon.
In terms of market performance, Uniswap remains one of the most active protocols in decentralized finance. According to Token Terminal, Uniswap recorded its highest-ever monthly trading volume in October 2025, reaching roughly USD 116.6 billion. Data from DefiLlama also shows that Uniswap continues to rank as the largest decentralized exchange by trading activity, consistently processing more volume than any other on-chain venue. This sustained usage underscores Uniswap’s position as a core liquidity layer across Ethereum and the broader Layer-2 ecosystem.
How Does Uniswap Work with AMM and Liquidity Pools?
Uniswap works by replacing traditional order books with on-chain smart contracts that automate pricing, liquidity management, and trade execution. Instead of matching buyers and sellers, the protocol allows users to trade directly against token reserves stored in smart contracts. Its design is built on two mechanisms that enable permissionless and continuous trading across Ethereum and major Layer-2 networks: an
automated market maker (AMM) that sets prices algorithmically and Uniswap liquidity pools that supply the assets used for swaps.
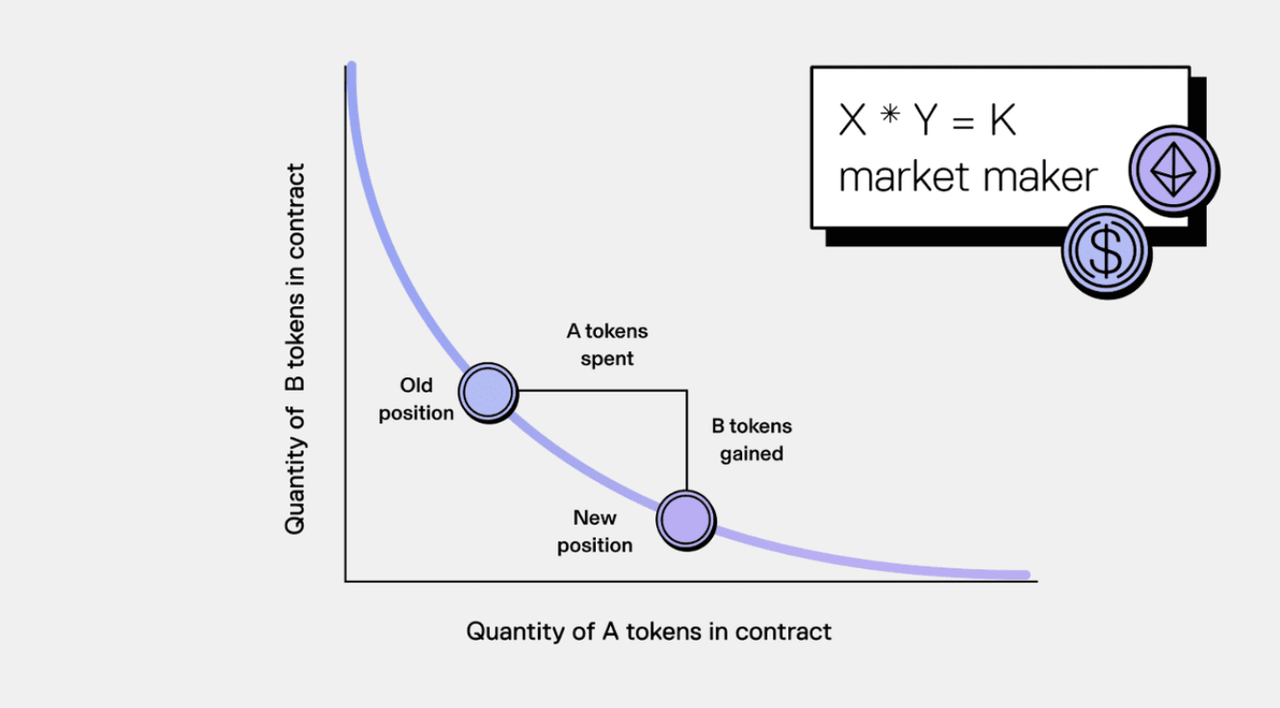
Automated Market Makers (AMM): The AMM uses the constant-product formula "x · y = k" to determine token prices. As trades occur, the ratio between the two tokens changes, and the AMM adjusts the price automatically to maintain the constant product. This approach removes the need for order books and ensures that trades can be executed at any time.
Uniswap Liquidity Pools: Liquidity pools are created when users deposit a pair of tokens into a smart contract. Traders swap against these reserves, and each trade changes the pool’s balances according to the AMM formula.
Liquidity providers earn fees from the trading activity, and larger pools generally offer more stable prices with lower
slippage.
When a user initiates a swap, the AMM and liquidity pool interact through the following sequence:
1) A user selects two tokens to swap, initiating a trade through the AMM interface.
2) The AMM routes the trade to the liquidity pool holding that token pair.
3) The smart contract applies the AMM formula to calculate the output amount.
4) The liquidity pool updates its token balances to reflect the trade.
5) Liquidity providers receive their share of trading fees.
Together, these steps allow Uniswap to operate as a fully decentralized crypto trading system. The AMM provides real-time pricing, the liquidity pools supply the assets, and the smart contracts ensure that trades settle seamlessly without intermediaries.
Uniswap V1 to V4 Overview: Main Feature Updates and Key Differences
Since its launch in 2018, Uniswap has evolved through four major versions, each addressing important limitations of the earlier model. These upgrades transformed Uniswap from a simple automated market maker into a more flexible and programmable liquidity framework. Together, V1 to V4 trace how the protocol grew into the most widely used decentralized exchange across Ethereum and major Layer-2 networks.
1. Uniswap V1 – The First Automated Market Maker on Ethereum
What Uniswap V1 Solved: Introduced permissionless token trading without order books
Uniswap V1 launched in November 2018, marking the beginning of AMM-based decentralized trading on Ethereum. At a time when most decentralized exchanges relied on order books or complex matching systems, V1 introduced a simple but powerful model where users could trade directly against on-chain reserves. This early version demonstrated that a decentralized exchange could operate entirely through smart contracts, without custodial risk or centralized control. Although minimal in design, V1 built the foundation for the entire AMM ecosystem and proved that permissionless liquidity creation could support real trading activity.
Main Features of Uniswap V1
• ETH as the base asset: All pools were structured as ETH–ERC20 pairs, so ERC20-to-ERC20 trades had to route through ETH.
• Permissionless pool creation: Anyone could create a pool and add liquidity by depositing ETH and an ERC20 token.
• Minimal contract design: A simple architecture that kept V1 accessible and easy to audit.
• First real AMM on Ethereum: Proved that on-chain liquidity could function at scale.
Limitation: Only supported ETH–ERC20 pairs, increasing slippage and gas costs for ERC20-to-ERC20 swaps.
2. Uniswap V2 – Direct ERC-20 Swaps and Better Oracles
What Uniswap V2 Solved: Enabled efficient ERC20-to-ERC20 trading and improved price reliability
Uniswap V2 launched in May 2020, introducing key upgrades that removed V1’s biggest constraints. It enabled direct ERC20-to-ERC20 swaps, improved oracle functionality, and added features that supported more advanced DeFi interactions. V2 quickly became the dominant AMM design during the 2020–2021 DeFi surge, powering much of the early yield farming and lending ecosystem. Its improvements made Uniswap significantly more flexible, composable, and efficient, cementing its role as a core DeFi infrastructure layer.
Main Features of Uniswap V2
• Direct ERC20-to-ERC20 trading: Eliminated the need to route through ETH for token-to-token swaps.
• Time-weighted average price oracle: Built-in TWAP oracles provided more manipulation-resistant pricing.
• Flash swaps: Allowed users to withdraw tokens with no upfront cost if returned in the same transaction.
• Modular contract design: Separation of core and periphery logic improved integration for developers.
Limitation: Capital remained spread across the entire price curve, which limited capital efficiency.
3. Uniswap V3 – Concentrated Liquidity for Maximum Efficiency
What Uniswap V3 Solved: Made liquidity far more capital efficient and customizable
Uniswap V3 went live on May 5, 2021, introducing concentrated liquidity, one of the most significant AMM innovations to date. Instead of distributing liquidity uniformly across all price levels, V3 allowed providers to choose precise price ranges, dramatically improving the usability of their capital. This upgrade made it possible to deliver deeper liquidity with far less total value locked. V3 also added multiple fee tiers, improved oracle design, and made liquidity positions non-fungible, enabling more sophisticated and optimized LP strategies.
Main Features of Uniswap V3
• Concentrated liquidity: LPs allocate capital within specific price ranges for greater efficiency.
• Multiple fee tiers: Pools offer fee options tailored to volatility and LP risk preference.
• Non-fungible LP positions: Each LP position is represented as an NFT due to unique parameters.
• Improved TWAP oracles: More accurate and cost-efficient pricing data for external protocols.
• Higher capital efficiency: Smaller pools can achieve deeper liquidity with significantly less capital.
Limitation: LP positions require active management and can fall out of range, generating no fees.
4. Uniswap V4 – A Customizable Liquidity Framework
What Uniswap V4 Solved: Enabled programmable liquidity and reduced gas costs for new pools
Uniswap V4 officially launched on January 31, 2025, introducing an architecture focused on customization, scalability, and gas efficiency. With its new hook system, V4 allows developers to insert custom logic into pool actions, enabling dynamic fees, custom AMM curves, on-chain limit orders, time-weighted liquidity, and more advanced trading behaviours that were not possible in earlier versions. The shift to a singleton contract architecture brings all pools under one contract, reducing deployment costs and making routing more efficient. Native ETH support further simplifies liquidity provision by removing the need for wrapped assets. V4 marks a shift from a single AMM model to a fully programmable liquidity framework that developers can tailor to specific use cases across Ethereum and Layer-2 networks.
Main Features of Uniswap V4
• Singleton contract architecture: All pools are contained in one contract, lowering the cost of deployment and interaction.
• Native ETH support: Users can provide ETH directly without wrapping into
WETH.
• Flash accounting: State updates occur at transaction end, lowering gas usage.
• Highly flexible design: Enables creation of custom AMM models and advanced on-chain trading features.
Limitation: Increased flexibility introduces more complexity and requires careful security considerations.
Uniswap V1 vs V2 vs V3 vs V4: A Complete Side-by-Side Comparison
Uniswap’s four versions introduce different architectures, AMM mechanics, and liquidity models. Each upgrade solves specific limitations of the previous design and improves how the protocol handles pricing, liquidity, and efficiency. The table below summarizes the core differences between V1, V2, V3, and V4.
| Category |
Uniswap V1 |
Uniswap V2 |
Uniswap V3 |
Uniswap V4 |
| Launch Year |
2018 |
2020 |
2021 |
2025 |
| Architecture |
Minimal contracts |
Modular design |
Range-based AMM |
Singleton with hooks |
| Trading Model |
ETH-routed swaps |
Direct ERC20–ERC20 |
Optimized routing |
Programmable routing |
| AMM Design |
Constant-product |
Constant-product |
Concentrated liquidity |
Custom AMMs via hooks |
| Liquidity Model |
Single pool |
Single pool |
Price-range liquidity |
Hook-based behaviors |
| Capital Efficiency |
Low |
Medium |
Very high |
Variable |
| LP Positions |
Fungible |
Fungible |
NFT positions |
Configurable |
| Fees |
Fixed |
Fixed |
Multiple tiers |
Fully customizable |
| Supported Networks |
Ethereum only |
Ethereum only |
Ethereum + major L2s |
Ethereum + expected L2 deployments |
| Price Oracles |
None |
TWAP oracle added |
More efficient TWAP, granular |
Oracle extensions through hooks |
| Developer Extensibility |
Very limited |
Moderate via routing |
Moderate via LP strategy options |
Extensive, programmable hooks |
| Key Improvement |
Enabled permissionless AMM trading |
Efficient ERC20 swaps + flash swaps |
High capital efficiency |
Customizable pools + lower gas |
| Main Limitation |
Only supports ETH routing |
Liquidity inefficient across full curve |
Requires active LP management |
Higher complexity + security concerns |
How to Buy and Trade Uniswap (UNI) on BingX
BingX supports UNI on both Spot and Futures markets, making it easy to build long-term positions or trade short-term price movements.
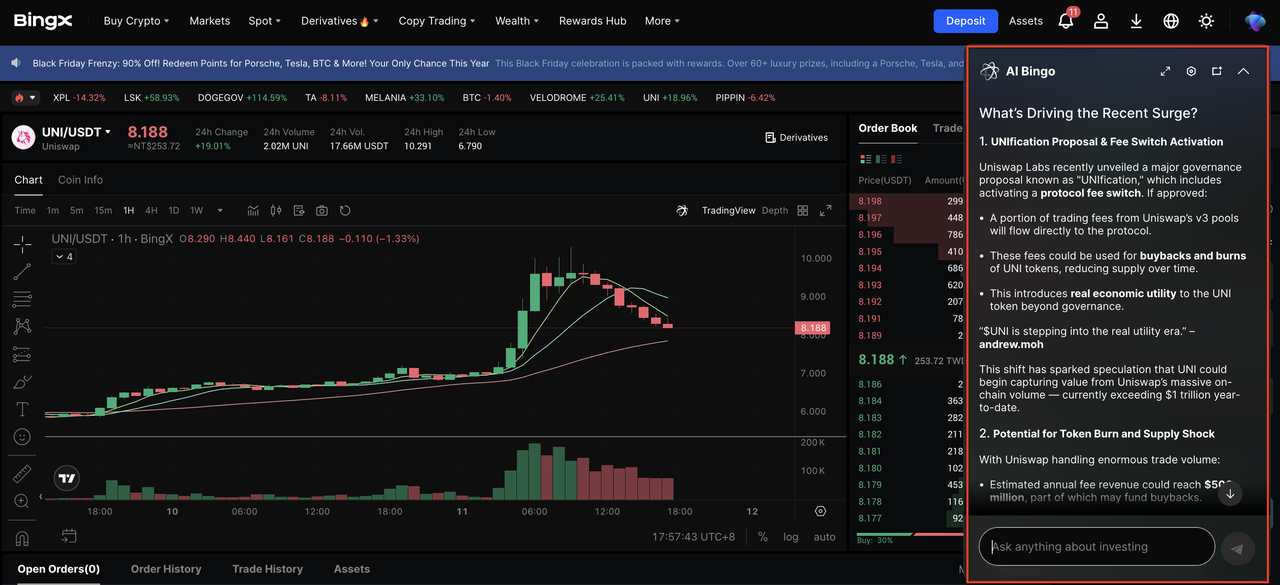
BingX AI is integrated directly into the chart to help identify support and resistance, breakout zones, and potential entry ranges.
Step 2: Activate BingX AI Click the AI icon on the chart to access real-time insights, including key price levels and trend analysis.
Step 3: Choose Spot or Futures Use Spot if you want to accumulate UNI. Use Futures if you want to trade short- or long-term moves with the option to go long or short.
Step 4: Place Your Order Select a market or limit order. For Futures, set leverage and configure
stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Step 5: Manage Your Position Spot purchases appear in your BingX wallet. Futures positions can be monitored and adjusted within the trading interface.
Conclusion
Uniswap’s four versions show how the protocol expanded from a simple constant-product AMM into a programmable liquidity framework. V2 introduced efficient ERC20 swaps, V3 improved capital efficiency with concentrated liquidity, and V4 added customizable pool logic and lower gas through its singleton architecture. These upgrades helped Uniswap become a core liquidity layer across Ethereum and major Layer-2 networks. As V4 adoption grows, the protocol is positioned to remain a leading AMM infrastructure for on-chain trading.
Related Reading