NVIDIA (NVDA) didn’t just shape gaming but also built the backbone for the modern AI era. Since its IPO in 1999, NVIDIA evolved from a GPU-maker into the world’s leading
AI compute infrastructure company. As generative AI exploded in 2022–2025, hyperscalers and cutting-edge labs loaded up on its H100, Blackwell and next-gen GPUs. In Q3 FY25 alone, NVIDIA delivered a stunning $57.0 billion in revenue and $31.9 billion in net income, up 62% and 65% year-on-year respectively, with data-center sales driving the surge.
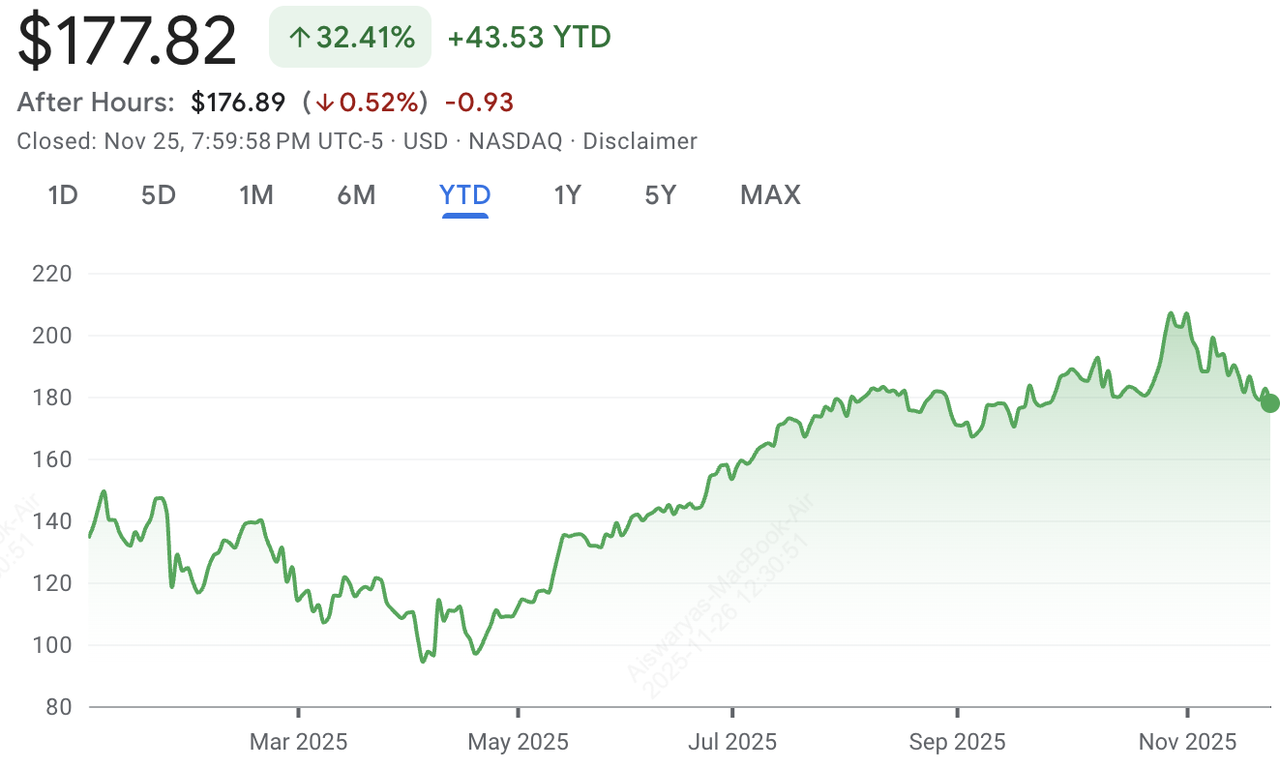
NVDA stock performance in 2025 | Source: Google Finance
In October 2025, NVIDIA became the first public company ever to hit a $5 trillion market cap, surpassing
Apple (AAPL),
Microsoft (MSFT),
Alphabet (GOOGL), and
Amazon (AMZN). That milestone reflects how deeply its chips and software are woven into global AI infrastructure, enabling everything from cloud computing and robotics to autonomous systems and large-scale scientific research.
In this article, you will learn how to invest in Nvidia (NVDA) stock in 2025 through direct brokerages, ETFs, and crypto-based
tokenized NVDA on BingX.
What Is NVIDIA and What Does NVIDIA Do?
NVIDIA (NVDA) is an American semiconductor and computing company founded in 1993 and headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It started with a clear goal: build processors that handle visual and parallel computing far better than traditional CPUs. That vision led to the first widely adopted graphics processing units (GPUs) and laid the groundwork for today’s AI accelerators.
Over time, NVIDIA evolved from a pure graphics chip designer into a full-stack accelerated computing company. It now designs GPUs, server platforms, networking hardware and an extensive software ecosystem, including the CUDA programming model and specialized AI frameworks. These tools make it easier for developers and enterprises to train large models, run inference at scale and accelerate high-performance computing workloads.
As of 2025, NVIDIA’s business is organized around several major segments:
• Data Center and AI: NVIDIA’s largest and fastest-growing segment. It supplies GPUs, full server systems and high-speed networking that power AI training, inference and large cloud data centers. In the latest reported quarter, data center revenue reached about $51.2 billion, up 66% year-on-year, highlighting how quickly AI infrastructure spending is scaling.
• Gaming: Still a key revenue driver, built around GeForce GPUs, gaming laptops, software like GeForce Experience and cloud gaming services. These products serve both casual and competitive gamers worldwide.
• Professional Visualization: GPUs, platforms and software for designers, engineers and content creators. This segment supports CAD, 3D design, media production and enterprise visualization workflows.
• Automotive: Focused on in-vehicle AI, driver-assistance and autonomous driving systems, as well as simulation platforms used by automakers and robotaxi developers.
Across these segments, NVIDIA is no longer just a “graphics card” company. It operates at the intersection of chips, networking, systems and software, providing the core compute layer that runs modern AI and accelerated applications. For you as an investor, this means NVIDIA’s growth is tied directly to long-term trends in AI, cloud computing and data-center demand rather than only to PC or console gaming cycles.
Who Are NVIDIA's Key Partners and Competitors to Watch in 2025?
NVIDIA’s position in the AI industry is shaped by a powerful network of partners that depend on its GPUs and a growing group of rivals building competing AI chips.
Key Partners: Who Builds the AI Boom on NVIDIA?
NVIDIA’s GPUs power the largest AI clusters in the world, supported by major partners such as OpenAI, Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Meta, all of which rely on NVIDIA hardware for large-scale training and inference. These cloud and AI leaders continue to expand GPU super-clusters, reinforcing NVIDIA’s ecosystem lock-in across software, hardware, and infrastructure. According to IoT Analytics (2025), global data-center infrastructure spending hit $290 billion in 2024, with 78% directed toward IT hardware like GPU-rich servers, making NVIDIA the primary beneficiary of the AI-compute surge.
Main Competitors: Who’s Trying to Dethrone NVIDIA in 2025?
Despite its dominance, NVIDIA faces intensifying competition. AMD’s Instinct MI300/MI325 accelerators are gaining traction in data-center AI workloads. Google continues pushing its custom TPU lineup (including the 2025 “Ironwood” generation), while AWS expands its Trainium and Inferentia chips to reduce reliance on third-party GPUs. Several emerging AI-chip startups are also building specialized, power-efficient ASICs for inference-heavy workloads. Omdia estimates NVIDIA still holds around 80% of the AI-accelerator market, but growing demand for cost-efficient and vertically integrated infrastructure is slowly increasing adoption of alternative silicon.
What This Means for NVIDIA’s Strategic Position in 2026
By 2026, NVIDIA’s strategic position remains exceptionally strong, anchored by its CUDA ecosystem, software stack, and unmatched developer adoption, advantages that still make switching costly for most AI builders. Yet the competitive landscape is shifting faster: Google’s next-gen TPUs, AWS’s expanding Trainium lineup, AMD’s improved MI300-series successors, and a wave of specialized AI ASICs are giving hyperscalers and enterprises more credible alternatives.
As AI workloads diversify and cost efficiency becomes a core priority, NVIDIA is expected to stay the leading provider of frontier AI compute, but its near-total dominance may soften in 2026 as cloud providers mix in more in-house silicon to reduce reliance, manage costs, and optimize specific AI tasks.
How to Invest in NVIDIA Stock: A Step-by-Step Guide
Investors today have multiple ways to gain exposure to NVIDIA (NVDA), from traditional equity ownership to modern crypto-native options. Choose based on your goals: full shareholder rights, easy global access, or flexibility and leverage via tokenized assets.
1. Buy NVIDIA Shares (NVDA) on a Brokerage Platform
If you want direct ownership, full rights (dividends, corporate governance), and long-term equity exposure, this is the classical route. Here's how to buy NVDA shares via a brokerage platform like Fidelity, Charles Schwab, Robinhood, eToro, and Webull:
1. Open a brokerage account: Select a regulated platform that offers access to U.S. equities, transparent fees, USD funding options and stable trading tools.
2. Complete KYC and fund account: Complete registration by submitting identification documents, passing KYC checks and filling in tax forms required for non-U.S. investors.
3. Buy NVDA Stock: Search for ticker “NVDA” on the brokerage platform. You can purchase full shares or fractional shares. Some brokers allow investing with as little as $1.
4. Take key considerations into account: Before you invest, consider tax rules, currency exchange rate fluctuations, and the annual foreign-remittance limit under regulatory schemes as a non-U.S. investor.
Why Buy NVDA Stock on Brokerages
• Full ownership: dividends (subject to withholding), voting/legal rights as a shareholder.
• No counterparty or tokenization risk, you hold actual shares.
• Clean regulatory status under U.S. and international securities laws.
2. Buy Tokenized NVIDIA Stock (NVDAon / NVDAX) on BingX Spot
NVDAON/USDT trading pair on the spot market powered by BingX AI insights
If you want global access to NVIDIA exposure without a U.S. brokerage account, BingX makes it easy to
buy tokenized NVDA directly on the Spot market. Follow these steps to buy tokenized NVIDIA stock on BingX:
1. Sign and verify a BingX account: Create a BingX account and complete quick KYC to unlock full Spot trading access.
2. Fund your BingX account: Deposit USDT using your preferred network (TRC20, ERC20, etc.) and confirm the funds in your Spot wallet.
4. Place a buy order: Choose
Market for instant execution or Limit if you want a specific entry price.
5. Monitor your NVDA portfolio: Track your holdings using
BingX’s AI-powered insights to monitor support levels, volatility, and trend strength.
Why Choose BingX for Tokenized NVIDIA?
• Start with as little as $10 via fractional trading.
• No U.S. brokerage, no USD funding, no cross-border paperwork.
• 24/7 global access, fast execution, and seamless integration with your existing crypto portfolio.
3. Trade NVIDIA Tokenized Stock Futures on BingX
NVDAX/USDT perpetual contract on the futures market powered by BingX AI
For active traders, BingX offers NVIDIA tokenized stock perpetual futures, giving you long/short flexibility and leverage, all without holding the underlying tokenized asset.
BingX futures replicate NVDA price movements through perpetual contracts, allowing up to high leverage with USDT margin. This lets you trade short-term moves, hedge spot positions, or profit in either direction of the market. Here's how to trade NVDA tokenized stock on the BingX futures market:
1. Enable Futures trading inside your BingX account.
2. Transfer USDT to your Futures wallet as collateral.
4. Open a long or short position, choose your leverage, and confirm the order.
5. Manage your trade with
stop-loss, take-profit, margin alerts, and AI-guided insights directly inside BingX Futures.
Why Trade NVDA Futures on BingX?
• Go long or short to trade any market condition.
• Use leverage for greater capital efficiency.
• Built-in BingX AI tools help identify trends, volatility zones, and risk levels.
Risks to Consider: Futures involve leverage, which magnifies losses. Tokenized-stock derivatives may have higher volatility, liquidity differences, and do not provide shareholder rights or dividends.
NVDA Shares vs. NVDA Tokenized Stocks: Which Option Should You Choose?
The best way to invest in NVIDIA depends on your goals: choose a traditional brokerage if you want full shareholder rights and long-term equity ownership; pick tokenized NVDA on BingX if you prefer low entry barriers, global access, and simple USDT-based trading; and use NVDA perpetual futures on BingX if you’re an experienced trader looking for leverage, long-short flexibility, or short-term strategies.
| Investor Profile |
Recommended Route |
| Long-term investor seeking real-ownership, dividends, legal rights |
Buy NVDA shares on traditional brokerages |
| Crypto user or global investor with small capital or seeking 24/7 trading |
Tokenized NVDA stock like NVDAX and NVDAon |
| Trader or hedger comfortable with leverage and higher risk |
Tokenized NVDA Futures |
What Is NVIDIA Tokenized Stock (xStock), and How Does It Work?
Tokenized NVIDIA stock gives you blockchain-based exposure to NVDA’s price without needing a U.S. brokerage account, offering fractional access, global availability, and 24/7 trading. These tokens, such as NVDAx or NVDAon, fit naturally into the crypto ecosystem, allowing investors to start with small amounts, hold NVDA alongside digital assets, and benefit from fast transfers and wallet integration across supported platforms.
How NVIDIA xStock Works
• Blockchain-based representation: A
tokenized share is a digital token on a blockchain like Ethereum or Solana that reflects the value of a real NVIDIA share. Typically, a regulated custodian holds the actual NVDA share (or equivalent collateral), and issues a corresponding token on-chain, creating a 1:1 (or fractional) peg between token and share.
• Fractional and global access: Because tokens can be split into small units, you don’t need capital for a full NVIDIA share; often you can invest with as little as a few dollars or stablecoin, e.g. USDT. This opens up U.S. equity exposure to global and retail investors without needing a U.S. brokerage account.
• Continuous, flexible trading: Unlike traditional stock markets limited to U.S. trading hours, tokenized NVIDIA can trade 24/7 or 24/5, offering global users flexibility across time zones and allowing instant settlement via blockchain rather than T+2 clearing.
• Digital-native integration: Tokens integrate with crypto wallets, allowing you to hold, transfer, or trade the exposure within a broader digital-asset ecosystem, useful for users who already trade or hold crypto.
Key Factors to Consider Before Investing in Tokenized NVIDIA Stock
Before buying tokenized NVIDIA, it’s important to understand the structural and regulatory trade-offs that make these digital assets different from holding real NVDA shares.
1. No shareholder rights: Tokenized NVDA gives you price exposure only, and not ownership of actual shares, so you don’t receive voting rights, and dividend treatment depends entirely on the issuer’s design.
2. Issuer and custody risk: Your exposure relies on the issuer or custodian properly backing the tokens; poor collateral management or operational issues can cause the token’s price to drift away from real NVDA.
3. Regulation and liquidity limits: Tokenized stocks operate in developing regulatory frameworks, and liquidity comes from the exchange rather than a major stock market, which can lead to wider spreads, lower protections, and different trading behavior during volatile periods.
Final Thoughts: Should You Invest in NVIDIA Shares or Tokenized NVIDIA?
Whether you choose traditional NVDA shares or tokenized NVIDIA depends on your goals, risk tolerance, and preferred investment environment. If you want long-term ownership, shareholder rights, dividends, and the regulatory protections of U.S. equity markets, buying NVIDIA stock through a brokerage is the more suitable option. It offers full exposure to the company’s fundamentals, but may require higher capital, USD funding, and cross-border compliance depending on your country.
If you prefer easier access, fractional investing, or 24/7 global trading, tokenized NVIDIA provides a flexible, crypto-native alternative that mirrors NVDA’s price without needing a U.S. brokerage account. However, these tokens only offer economic exposure, not actual share ownership, and come with issuer risk, different liquidity dynamics, and evolving regulatory treatment.
As with all investments, both formats carry market risk, and tokenized assets introduce additional structural risks. Always assess your financial objectives, understand platform-specific mechanics, and avoid investing more than you can afford to lose.
Related Reading