The numbers tell you how big this has become:
Bitcoin mining still consumes well over 100 TWh of electricity a year, while Ethereum’s move to proof-of-stake cut its energy use by 99.9%. On the staking side,
liquid-staking protocols alone now hold tens of billions of dollars in TVL, with
Lido with over $40 billion and more than 9 million
ETH staked through it in 2025.
This guide compares cloud mining vs. staking across mechanics, profitability, risk, sustainability, and regulation so you can decide which better fits your passive income strategy in 2026.
Why Is Everyone Comparing Cloud Mining and Staking in 2026?
The mining-vs-staking debate is back because the macro and tech backdrop changed:
• Post-2024 Bitcoin halving: Rewards dropped to 3.125 BTC per block, squeezing miner margins and cloud-mining profitability.
• PoS dominance is growing: PoW networks still account for roughly 60% of crypto market cap, but PoS and
staking tokens are rapidly gaining share as new projects launch on PoS rails.
• Liquid staking has exploded: Liquid-staking TVL exceeded $80–90 billion in 2025, with Lido alone above $41 billion and holding around 30% of all staked ETH.
• Environment and regulation: Governments are scrutinizing energy-heavy mining, while staking-as-a-service and liquid-staking tokens are getting their own regulatory treatment in the US and EU.
So the real question for 2026 is not just “Which pays more?” but “Which gives you the best risk-adjusted return, with acceptable liquidity and regulatory risk?”
What Is Cloud Mining?
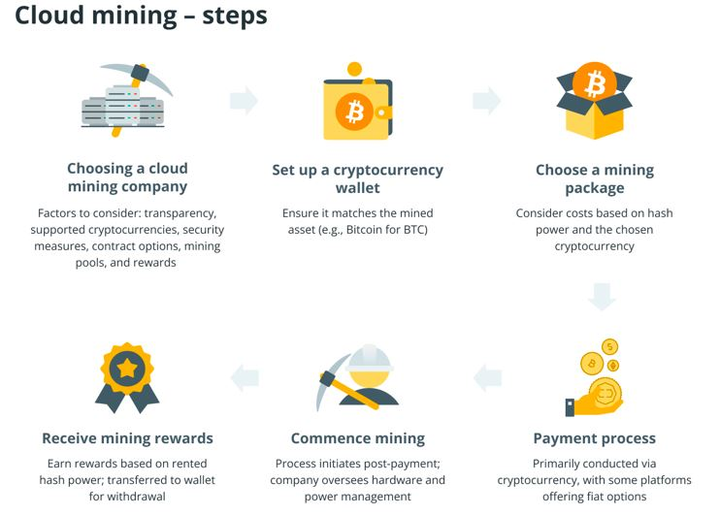
How cloud mining works | Source: SunCrypto Academy
Cloud mining lets you rent Bitcoin mining power from a remote data center so you don’t need to buy or operate expensive ASIC machines at home. In simple terms, a cloud-mining provider runs the hardware, sells you a contract based on hash rate (TH/s) and duration - typically 12–36 months, and then pays you a share of the Bitcoin mined after deducting electricity, cooling, maintenance, and platform fees. Because these costs are high, even reputable platforms like ECOS or HashNest generally produce 5–10% APR in realistic market conditions, much lower than the unrealistic “guaranteed high-profit” claims often seen on scam sites.
Key Benefits of Cloud Mining
1. No hardware hassle: You don’t manage rigs, cooling, or noise. The provider runs everything.
2. Bitcoin-native yield: You earn BTC directly, which some investors prefer over PoS tokens.
3. Predictable contract terms: Fixed duration and hash rate, useful if you want a defined exposure window.
Trade-offs and Red Flags in Cloud Mining
1. High scam risk: Cloud mining has a long history of Ponzi schemes, e.g., BitClub Network’s $700 million fraud, and fake “cloud mining dashboards” are a common scam pattern.
2. Opaque costs: Electricity and maintenance fees can quietly eat most of your rewards, especially if BTC price or network difficulty moves against you.
3. Low liquidity: Once you pay for a contract, you often can’t exit early.
4. Regulatory and energy pressure: Jurisdictions with tight energy or AML rules may restrict mining operations, adding business-continuity risk.
For most retail users, cloud mining offers a high-risk, low-control exposure to Bitcoin’s proof-of-work economy.
What Is Crypto Staking?
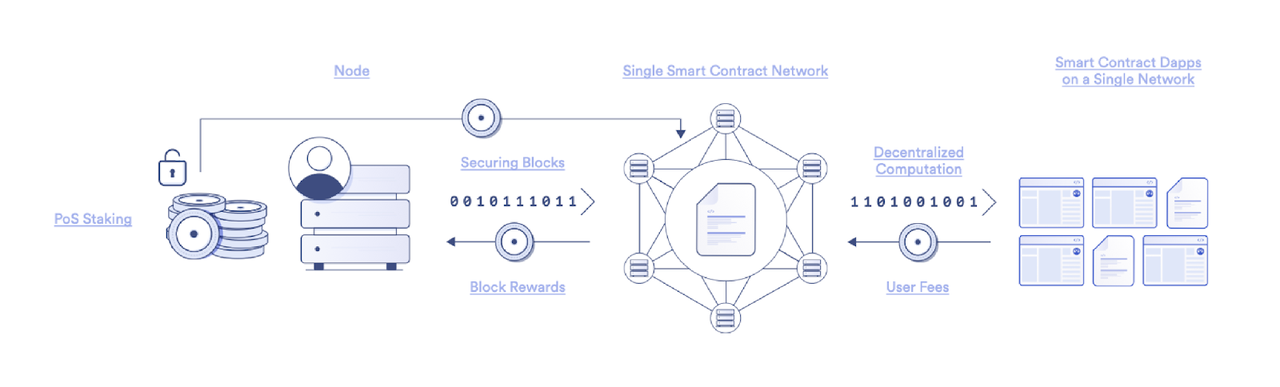
How staking works | Source: Chainlink
Staking lets you lock your crypto to help secure a proof-of-stake blockchain, such as Ethereum, Solana, or
Cosmos, and earn rewards for contributing to network validation. Beginners usually stake through an exchange or liquid-staking protocol with just a few clicks, while advanced users can run their own validator, which requires higher capital, technical setup, and uptime management.
Staking rewards are paid out from network inflation, transaction fees, and sometimes MEV (maximal extractable value). As of 2025, typical yields are 3–4% APR for Ethereum, 6–7% for Solana, and higher for some smaller PoS networks, while liquid-staking services and MEV-boosted strategies can raise total returns into the 8–12%+ range depending on market conditions.
Key Benefits of Staking
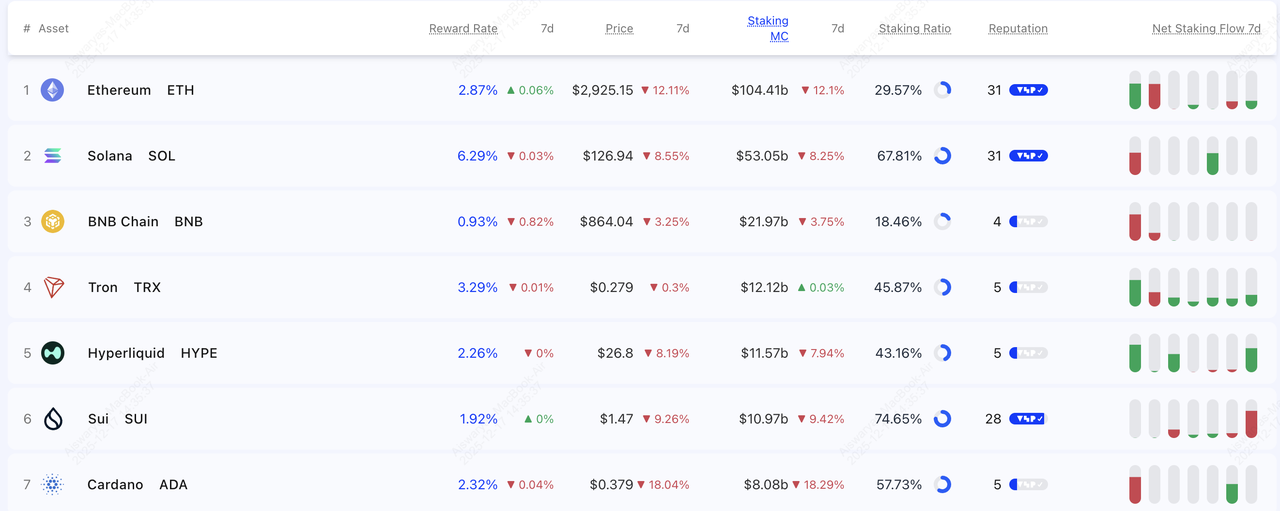
Rewards for top PoS tokens | Source: Staking Rewards
1. Low barrier to entry: You just need tokens and a supported wallet or exchange. No hardware.
2. More predictable yields: APYs are visible
on-chain and adjust gradually.
3. High flexibility: Many platforms offer flexible or short lock-up periods; liquid-staking tokens remain fully tradable.
4. Environment-friendly: PoS uses a fraction of PoW’s energy; Ethereum’s Merge cut its energy use by >99%.
Trade-offs of Staking
1. Price risk: If the token drops 50%, a 6% APY won’t save your principal.
2. Slashing and technical risk: Poorly run validators or buggy smart contracts (for liquid staking) can cause losses.
3. Regulation and tax: Some regulators treat staking rewards as income, and staking-as-a-service has attracted securities-law scrutiny.
On balance, staking offers cleaner, more transparent economics than cloud mining for most users.
Cloud Mining vs. Staking: A Side-by-Side Comparison
To help you quickly understand which passive income method delivers better value in 2026, here’s a clear side-by-side comparison of cloud mining and crypto staking across costs, risks, and real-world performance.
| Feature |
Cloud Mining |
Crypto Staking |
| Main idea |
Rent hash power from a remote data center to mine PoW coins (mainly BTC) |
Lock PoS tokens (ETH, SOL, ATOM, etc.) to secure the network and earn rewards |
| Typical real-world yield |
~5–10% APR on reputable BTC contracts, highlly variable |
~3–6% APR on ETH, 6–10%+ on SOL and some newer PoS chains |
| Upfront cost |
Prepaid contracts (hundreds to thousands of USD), no hardware ownership |
Just the tokens themselves, plus small network/exchange fees |
| Main risks |
Scam platforms, opaque fees, unprofitable contracts, counterparty risk, regulatory crackdowns on mining |
Token price drops, slashing (validator misbehavior), smart-contract risk for liquid staking |
| Liquidity |
Low – contract is usually locked; exiting early is hard or impossible |
Medium–High – unbonding delays on native staking; liquid staking tokens can trade instantly |
| Environment |
High energy use, can be carbon-intensive |
Very low energy use, ESG-friendly |
| Best for |
High-risk users who want BTC mining exposure without running hardware |
Most users who want predictable, flexible passive income in PoS ecosystems |
1. How Cloud Mining and Staking Actually Work: Core Mechanics Explained
Cloud mining lets you rent a fixed amount of Bitcoin hash power from a remote data center, which runs ASIC machines on your behalf. Your earnings come from your share of the mining pool’s block rewards minus electricity, cooling, and maintenance fees, which often account for 30–60% of gross revenue. Profitability changes daily based on Bitcoin’s price, network difficulty, and the efficiency of the miner your contract is tied to. In practical terms, if
BTC price drops or difficulty rises, your payouts can shrink quickly, even if you paid upfront for a long-term contract.
Staking involves locking your tokens, such as
ETH,
SOL, or
ATOM, to help secure a proof-of-stake blockchain, where validators are randomly selected to propose and verify new blocks. Rewards come from token inflation, transaction fees, and in some ecosystems, MEV (maximal extractable value) or restaking incentives, making yields more predictable than mining. Your actual return depends on the total amount staked on the network, the validator’s uptime and performance, and the token’s market price. For beginners, staking through an exchange or liquid-staking protocol is the simplest option and usually offers 3–12% APR depending on the asset and strategy.
2. Profitability in 2026: Cloud Mining's 5-10% APR vs. 3-12% Returns on Staking
BTC-focused cloud mining typically produces 5–10% APR in Bitcoin terms with reputable, long-running providers, after subtracting electricity, hosting, and maintenance fees that can consume a large share of revenue. However, your actual ROI in dollars can shift dramatically because profits depend heavily on Bitcoin’s price, network difficulty, and energy costs, all of which change frequently. Any platform claiming 100–800% guaranteed returns, fixed daily payouts, or “risk-free mining” almost always signals a Ponzi-style operation, since those numbers are impossible under real Bitcoin mining economics.
Real-world staking yields remain relatively stable and transparent, with 2024–2025 data showing 3–4% APR on Ethereum, 6–7% on Solana, and 10–15% on higher-inflation Cosmos-based chains. These returns can rise when you use liquid-staking tokens in DeFi or MEV-boosted strategies, pushing total yields into the 8–12%+ range for assets like SOL or
AVAX, but they also come with smart-contract and market risk. Because staking rewards are tied to protocol rules and validator performance, beginners generally see predictable payouts as long as the underlying token price remains healthy.
Takeaway: On a risk-adjusted basis, staking usually offers more stable and transparent returns, while cloud mining can underperform or even go negative after costs if BTC price or difficulty moves against you.
3. Cloud Mining's Hardware, Counterparty Risks vs. Staking's Smart Contract Risks
Cloud mining carries significant counterparty risk because you depend entirely on the provider’s honesty and operational transparency. U.S. Agencies, including the FBI, have repeatedly issued warnings about fake cloud-mining dashboards and platforms that disappear after collecting deposits, a pattern seen in several multi-million-dollar Ponzi schemes between 2022 and 2025. Even with legitimate providers, long-term contracts can become unprofitable overnight if Bitcoin mining difficulty spikes, post-halving rewards shrink, or electricity costs rise, leaving you locked into a losing agreement. There’s also regulatory and geographic risk: if the operator’s region imposes mining restrictions or energy curbs, your entire contract can halt with little recourse.
Staking removes hardware risk but introduces market and protocol risk; your staked tokens can drop 20–50% in a market downturn, wiping out months of yield regardless of the APR. Networks like Ethereum also enforce slashing penalties, meaning if your validator behaves incorrectly, both the validator and its delegators can lose a portion of their stake. Liquid-staking and restaking platforms add another layer of exposure: these protocols often hold billions in TVL, making them prime targets for smart-contract exploits or economic attacks. Finally, regulatory uncertainty remains: some jurisdictions are evaluating whether staking-as-a-service resembles an investment product, which could impact platform availability, reward structures, or compliance requirements over time.
In practice, cloud mining concentrates risk in the provider, while staking spreads risk across protocol design, validator performance, and token price.
4. Energy Impact and Sustainability: PoW vs. PoS in 2026
Bitcoin-style proof-of-work mining is highly energy-intensive, consuming roughly 100–170 TWh per year, similar to the electricity usage of countries like the Netherlands or Malaysia, with carbon impact varying sharply depending on whether miners operate in coal-heavy regions or renewable-powered hubs like Iceland. In contrast, proof-of-stake networks are dramatically more efficient: Ethereum’s move to PoS in 2022 reduced its energy consumption by ~99.95%, and most modern blockchains launch with PoS by default. As a result, staking requires little more than the energy of a standard server or validator node, making it far more sustainable and environmentally aligned for everyday users and institutions.
Key takeaway: If ESG or “green” mandates matter to you, staking wins clearly.
5. Cloud Mining Contract Fees vs. Staking Costs
Cloud mining typically requires prepaid contracts ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, plus recurring electricity and maintenance fees that can consume 30–60% of mining revenue depending on the provider and BTC difficulty. Staking, by contrast, only requires purchasing the token and paying small network or platform fees, often just a few cents to a few dollars, making it far cheaper to start and maintain for most users.
Staking or Cloud Mining: Which Is Better for You in 2026?
Choosing between cloud mining and staking in 2026 depends largely on your risk tolerance, technical comfort, budget, and long-term investment style.
1. Staking Is Best Suited for Beginners and Light-Asset Users
Staking is far easier for newcomers because you can start directly from an exchange or wallet without buying hardware or analyzing complex mining contracts. Yields are transparent, typically 3–12% APR depending on the asset, making it easier to estimate returns. Most importantly, staking avoids the high scam rate that plagues cloud mining, where fake dashboards and unrealistic payouts are common.
2. Cloud Mining and Advanced Staking for Tech-Savvy or High-Risk Investors
If you understand mining economics, difficulty charts, and fee structures, well-vetted cloud-mining contracts can provide BTC-denominated yield that behaves like leveraged Bitcoin exposure. These contracts are still risky, but technical investors may find them useful during bull markets or difficulty dips. On the staking side, advanced users can stack returns using MEV-boosted validators or restaking protocols, sometimes pushing yields into the 10–15%+ range—but with added smart-contract and liquidation risks.
3. Staking Crypto for Eco-Conscious and Long-Term Holders
Staking is the clear winner for sustainability, using over 99% less energy than Bitcoin mining following Ethereum’s 2022 transition to PoS. This makes it ideal for investors who want long-term, low-maintenance yield without the environmental footprint of PoW mining. It also aligns better with ESG-focused mandates and institutional frameworks.
4. Hybrid Strategy but Staking-Heavy for Professional Crypto Traders
Some investors choose to allocate a small portion of their portfolio to reputable cloud mining for BTC upside while putting the majority into staking across Ethereum, Solana, Cosmos, and liquid-staking platforms. This approach diversifies income sources between PoW and PoS systems, smoothing overall volatility. Staking remains the core driver of predictable passive income, while cloud mining serves as a higher-risk, BTC-focused complement.
How to Start Staking and Cloud Mining Crypto: Beginner's Guides
If you're ready to earn passive income but not sure where to begin, here’s a quick beginner-friendly guide to help you start staking or explore cloud mining safely.
How to Start Staking Crypto
Staking crypto on BingX Earn
If you want a simple way to earn passive crypto rewards, staking is the easiest place to start, and platforms like BingX Earn make the entire process beginner-friendly.
1. Choose your network and token. Beginners often start with large caps like ETH, SOL, ADA, or AVAX.
2. Pick your staking method
• Centralized exchange staking like BingX Earn: Platforms like
BingX Earn let you stake tokens with just a few taps, offering clear APRs, flexible or fixed-term options, and automated reward payouts. If you already trade on BingX, this is the fastest and simplest way to start earning staking rewards without managing validators or navigating on-chain tools.
• Liquid staking: Deposit tokens into a protocol, e.g.,
Lido-style platforms, and receive a liquid staking token you can use in DeFi.
3. Check APY, lock-ups, and fees. Compare reward rates, minimum amounts, unbonding periods, and any platform commissions.
4. Stake a test amount first. Start small to understand reward cadence, UI, and any gas fees.
5. Diversify validators and platforms. Avoid delegating everything to a single validator or protocol; this reduces slashing and smart-contract concentration risk.
Tip: On an exchange like BingX, the process typically looks like: create and verify your account, deposit or buy PoS tokens on spot, go to the Earn/Staking section, pick a product (flexible or fixed), and subscribe with the amount you want to stake.
How to Get Started with Cloud Mining
If you decide to explore cloud mining despite the risks:
1. Run a simple sanity check first. Ask: “If I just
bought BTC and held it, would I likely earn more than this contract after all fees?” In many cases, spot BTC + staking elsewhere is simpler and safer.
2. Research only long-standing platforms. Look for years of operation, public company info, and verifiable data center photos or audits. Use independent reviews, not just affiliate blogs.
3. Avoid unrealistic promises. Claims of guaranteed double-digit daily returns, 100%+ per month, or “risk-free” mining are classic Ponzi-scheme red flags.
4. Understand all fees and contract terms. Include electricity, maintenance, management fees, and minimum payout thresholds in your ROI calculations.
5. Start tiny and treat it as high-risk. Only allocate money you can afford to lose. Diversify across strategies; don’t go “all-in” on one mining contract.
Risks to Keep in Mind When Staking or Cloud Mining for Passive Income
Before committing meaningful capital to either strategy, remember:
1. Crypto prices are volatile: A sharp market drawdown can erase months of yield.
2. No yield is guaranteed: APYs and mining ROI are projections, not promises.
3. Platform risk matters: Whether you’re using an exchange, DeFi protocol, or cloud-mining site, always consider hacks, insolvency, and regulatory shocks.
4. Tax rules vary by country: In many jurisdictions, both staking and mining rewards are taxable income when received; check local guidance or consult a tax professional.
Conclusion
Data from 2024–2025 suggests that staking remains the more accessible and stable passive-income method for most users in 2026. It offers predictable yields, typically in the 3–12% APR range depending on the asset and strategy, and requires no hardware, contracts, or energy costs. Staking is also backed by strong infrastructure support across centralized exchanges, liquid-staking protocols, and major PoS networks, making it easier for beginners to start earning with minimal setup. Its low environmental footprint and clearer reward mechanics further strengthen its appeal for long-term, hands-off investors.
Cloud mining, however, still appeals to users who specifically want Bitcoin-denominated yield and understand the economics behind hash rate, difficulty, and energy pricing. When carefully researched, reputable providers may offer 5–10% APR in BTC terms, but profitability can shift quickly with market changes, and the sector has a long track record of scams and overpromised returns. As with any yield strategy, both methods carry risk: token prices can fall, platforms can underperform, and returns are never guaranteed. Whichever approach you choose, diversify your holdings, use proper
risk management, and only invest amounts you can afford to lose.
Related Reading
FAQs on Cloud Mining or Staking Crypto in 2026
1. Is staking safer than cloud mining?
Generally yes, for most retail users. Staking on established PoS networks via reputable platforms has clearer economics and fewer outright scams than the cloud-mining sector, which has seen multiple high-profile Ponzi schemes and fake platforms.
2. Can I lose money when staking crypto?
Yes. Your tokens still face price volatility, and you may be exposed to slashing for validator misbehavior or smart-contract risk for liquid staking. However, you usually don’t face the same “platform disappears overnight” risk that is common in shady cloud-mining offerings.
3. Is cloud mining still profitable after the 2024 Bitcoin halving?
It can be, but margins are thin and highly sensitive to BTC price, difficulty, and electricity costs. Many “guaranteed profit” contracts look good on paper but become unprofitable once fees and changing network conditions are factored in.
4. Cloud mining or staking, which method is more environmentally friendly?
Staking. Proof-of-stake networks use orders of magnitude less energy than proof-of-work mining. Ethereum’s move to PoS is the best example, cutting its energy consumption by over 99%.
5. Should I combine cloud mining and staking for earning more passive income?
If your capital is small or you’re new, it’s usually better to start with staking only. More advanced users sometimes build a hybrid approach, BTC exposure via mining plus diversified staking in PoS networks, to balance long-term conviction with yield and flexibility.