Staking remains a cornerstone of Proof‑of‑Stake (PoS) crypto networks, offering passive rewards for supporting blockchain security. But not all staking methods are created equal. As of mid‑2025,
Ethereum leads the pack with over 37 million ETH staked, representing roughly 30% of its total supply, up from previous figures. Meanwhile, the average staking yield across major networks is approximately 6.8%, though it ranges significantly: Ethereum delivers around 4–5% APY,
Solana offers 5–7%, and certain emerging chains still provide 10–12% to attract early participants. These trends reflect the growing popularity and evolving dynamics of staking in today’s crypto market.
Here's a clear breakdown of liquid staking, native (traditional) staking, and pool staking, helping you choose the right strategy for your crypto goals.
What Is Staking and How Does It Work?
How crypto staking works | Source: The Motley Fool
Staking is a way to earn rewards by locking up your cryptocurrency to support the operations of a blockchain. It’s used by Proof of Stake (PoS) networks like Ethereum, Solana,
Cardano, and
Polygon, which rely on stakers, not miners, to validate transactions and keep the network secure.
Here’s how it works:
• When you stake, you commit your crypto (like ETH or SOL) to the network.
• In return, the blockchain rewards you with new tokens, usually called staking rewards.
• Why? Because your staked assets help validate transactions and prevent fraud. The more crypto you stake, the higher your chance of being selected to validate the next block.
What Are the Different Types of Staking Available?
Staking isn’t one-size-fits-all. While the goal - earning passive income by helping secure a blockchain, is the same, how you stake can vary depending on your technical skills, investment size, and need for liquidity. Today, there are three primary staking methods available to most crypto holders: native staking, pool staking, and
liquid staking. Each offers a different balance of rewards, flexibility, and risk. Here's what you need to know to make the right choice.
1. Native (Traditional) Staking
Native staking involves locking your tokens directly into the network, either by running your own validator node by staking 32 ETH on Ethereum or operating a Solana validator with 1 SOL minimum stake, or by delegating to an existing validator. It offers high rewards and low third-party risk, but your assets are locked and require either technical expertise or trust in a chosen validator.
2. Pool Staking
Pool staking lets you combine your crypto with other users in a shared validator, lowering the entry barrier and simplifying the process. Platforms like
BingX Earn make this approach beginner-friendly and accessible with no large capital requirements, though it still involves lock-up periods and some counterparty risk from the pool operator.
3. Liquid Staking
Liquid staking gives you a tradable token (LST) that represents your staked assets, allowing you to earn rewards while using the token in DeFi. Platforms like
Lido issue liquid staking tokens (LSTs) such as stETH, offering unmatched liquidity and capital efficiency, but with added risks like smart contract vulnerabilities and token depegging.
Why Does Crypto Staking Matter in 2025?
As staking continues to evolve, choosing between native, pool, or liquid staking isn't just a matter of preference; it's a strategic decision that impacts your liquidity, reward potential, and risk exposure. Here’s why it matters more than ever in 2025:
1. Liquidity vs. Yield: Balancing Flexibility and Returns
Traditional staking typically locks up your funds for days or even weeks. That’s fine if you’re a long-term holder, but not ideal if market conditions shift. Liquid staking solves this by issuing
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs), like stETH or rETH, that let you earn staking rewards while still using your capital in DeFi.
With $68.7 billion locked in liquid staking protocols as of August 2025, it’s clear this model is gaining traction. These LSTs can be traded, used as collateral, or deposited into liquidity pools, unlocking dual-earning potential: staking rewards
plus DeFi yields. For example, stETH holders can still earn around 2.68% APR on Ethereum while simultaneously earning extra yield on platforms like
Aave or
Curve.
2. Risk and Complexity: Know What You're Signing Up For
Each staking method comes with a different risk profile:
• Native staking is relatively straightforward. You either run a validator node or delegate your tokens. While it’s considered the most secure and protocol-native option, your tokens are locked and unavailable for trading or emergencies.
• Pool staking makes it easier for users with smaller holdings (e.g., <32 ETH) to participate, but your rewards and security depend on the pool operator’s performance. There’s also counterparty risk if the operator mismanages the funds or gets slashed.
• Liquid staking, while offering superior flexibility, introduces new layers of risk: smart contract vulnerabilities, token depegging, and reliance on third-party protocols. If the value of your LST (e.g., stETH) diverges from the underlying token (ETH), you may experience losses, especially in volatile markets.
3. Regulatory Clarity: A Green Light for Liquid Staking
In a landmark decision, the U.S. SEC confirmed on August 6, 2025, that Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) are not securities. This regulatory clarity is a major milestone; it removes legal uncertainty for platforms and investors, enabling institutional funds, banks, and wealth managers to explore liquid staking as a compliant yield-generation strategy.
This decision is already fueling growth: weekly liquid staking fees have crossed $40.9 million, and protocols are now generating over $3 million in weekly revenue, according to Staking Rewards. With regulatory friction out of the way, expect broader participation, better infrastructure, and more innovation across liquid staking platforms.
In 2025, your staking choice is no longer just about earning rewards, it's about optimizing capital, managing risk, and aligning with the new rules of Web3 finance. Whether you prioritize simplicity, decentralization, or liquidity, understanding the trade-offs behind each model is key to maximizing your crypto’s earning potential.
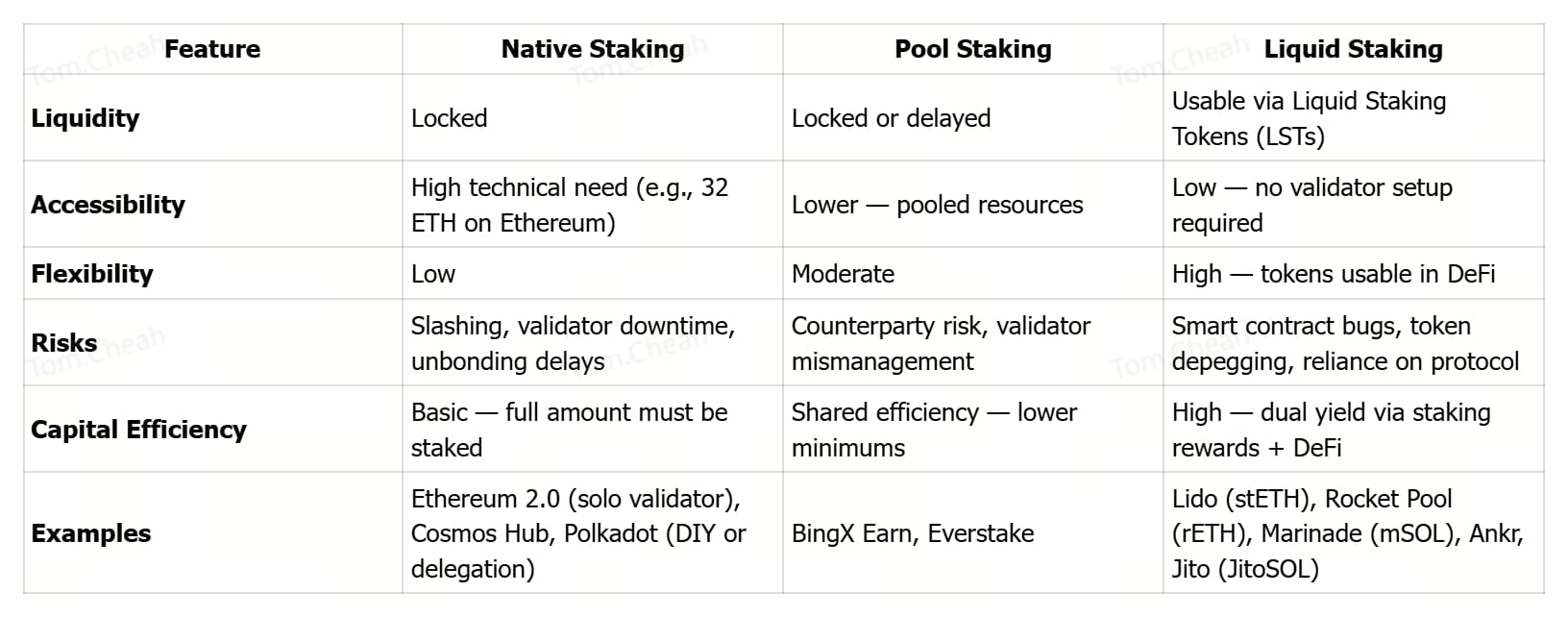
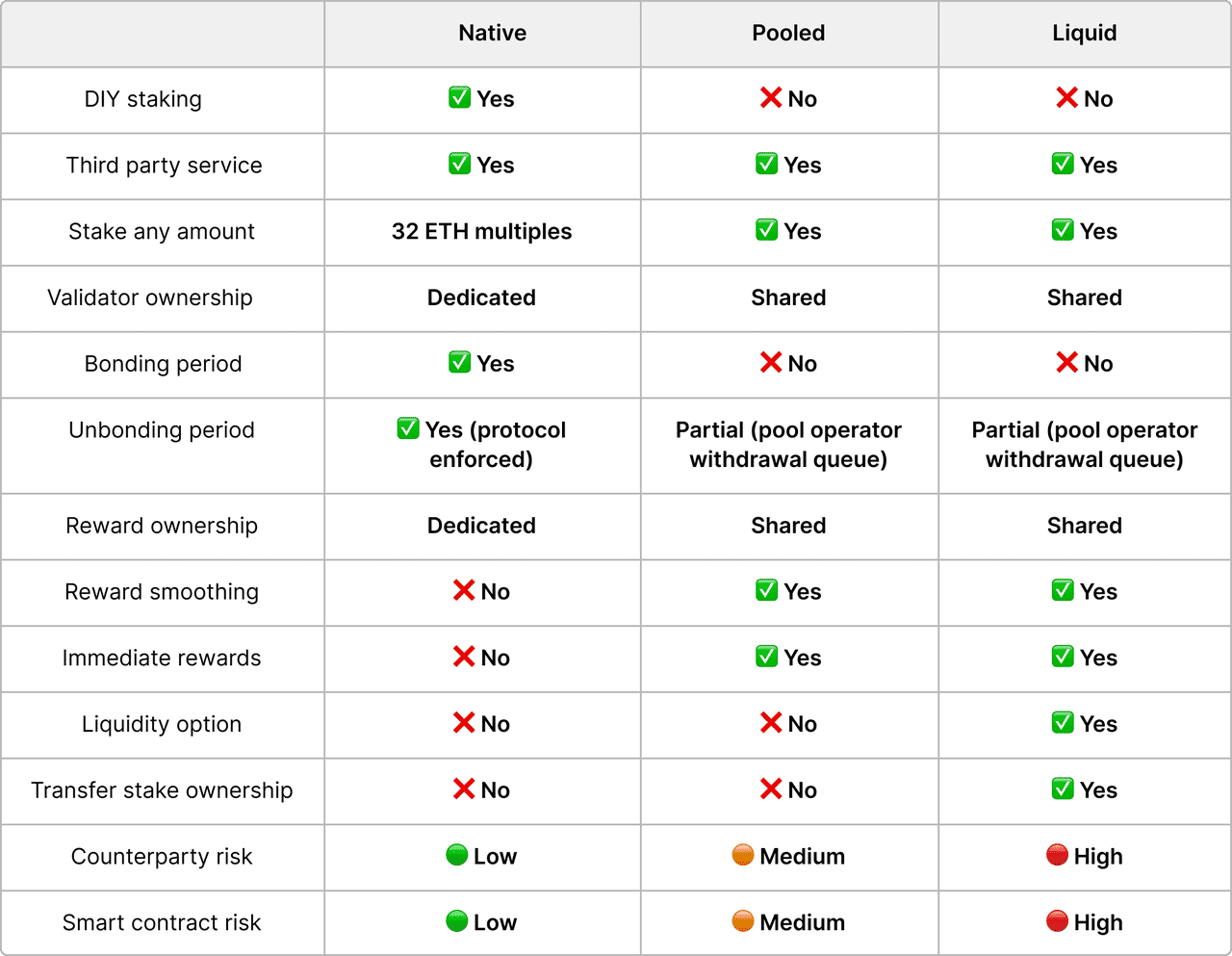
Liquid Staking vs. Traditional Staking vs. Pool Staking: A Comparison
Comparing liquid staking, traditional staking, and pool staking | Source: Kiln.fi
Choosing the right staking method depends on your capital size, risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and how actively you want to use your crypto while earning. Below is a detailed breakdown of native staking, pool staking, and liquid staking, how each works, their benefits and drawbacks, and when you should consider using them.
1. Native (Traditional) Staking
Native staking is the most direct and protocol-integrated form of staking. It involves locking your crypto directly into a blockchain’s smart contract to support its Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. You can either become a validator yourself, requiring technical expertise, a dedicated setup, and minimum capital (e.g., 32 ETH on Ethereum, 10,000 ADA on Cardano, or 1 DOT on Polkadot), or delegate your tokens to a validator node that performs staking on your behalf. Validators secure the network by validating blocks, and in return, both validators and delegators receive staking rewards.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Traditional Staking?
The biggest advantage of native staking is its security and simplicity; you're staking directly on the network, without relying on intermediaries. This reduces counterparty risk and often results in higher base rewards compared to other methods. However, it comes with major limitations: your tokens are locked for a set period, you may face unbonding delays, and if you’re running a validator, you’ll need to manage uptime and risk of slashing penalties for node misbehavior or downtime.
When to Choose Native Staking
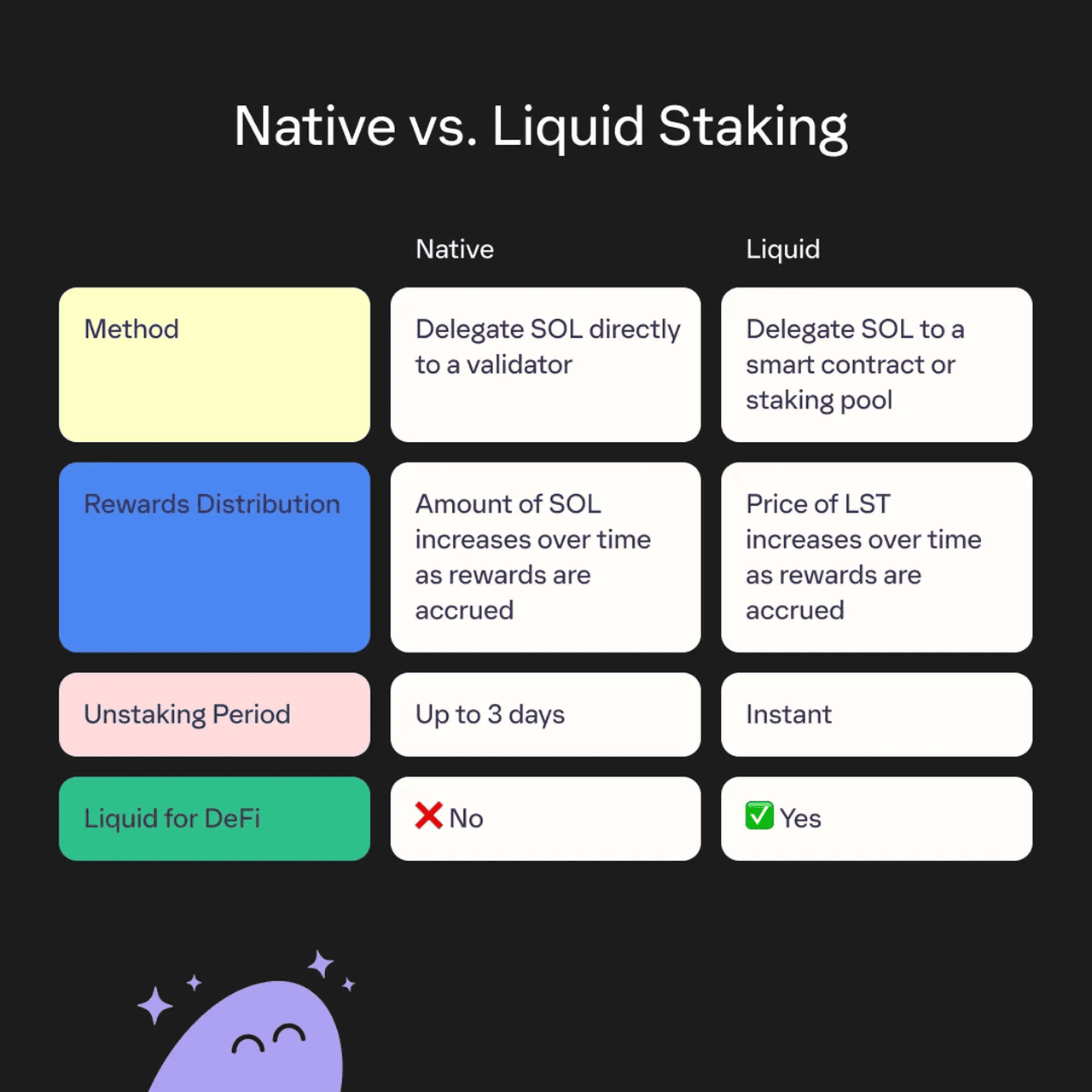
Native staking is ideal if you're a long-term holder with sufficient capital and a low need for liquidity. It suits investors who want maximum alignment with the network, and are either technically inclined or willing to delegate to reputable validators. If you’re comfortable not accessing your funds for weeks or months and value supporting decentralization, native staking is the most direct way to earn while contributing to blockchain security. Ethereum’s solo validator setup, Cardano’s delegation model, and Polkadot’s nomination system are prime examples of native staking in action.
Liquid vs. native staking | Source: Phantom Wallet
2. Pool Staking
Pool staking allows multiple users to combine their tokens into a shared staking pool, reducing the barrier to entry. These pools, available on platforms like BingX Earn and Everstake, manage the validator infrastructure on behalf of all participants. Even small token amounts (e.g., as low as 0.1
SOL or 0.01
ETH) can be staked through a pool, and rewards are distributed proportionally based on each user’s contribution.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Pool Staking?
Pool staking offers easy access and moderate returns with minimal setup required. It's especially attractive to non-technical users or those with small holdings. However, users still face asset lock-up periods and counterparty risk, since the pool operator controls validator selection and performance. Mismanagement or validator penalties could reduce your rewards or, in extreme cases, result in partial loss of funds.
When to Choose Pool Staking
Pool staking is a great option for users with modest portfolios who want to earn rewards passively without managing validators. It's ideal for those who value ease of use, are okay with some withdrawal delays, and prefer a trusted intermediary to handle the technical side. Popular examples include staking ETH or SOL via BingX Earn, or
ADA on Daedalus or Yoroi pools.
3. Liquid Staking
Liquid staking is the most flexible and capital-efficient staking model. When you stake through platforms like Lido,
Rocket Pool,
Marinade Finance, Ankr, or
Jito, you receive a Liquid Staking Token (LST), such as stETH (Lido), rETH (Rocket Pool), or mSOL (Marinade), that represents your staked asset. These tokens earn staking rewards and can be used across DeFi protocols for lending, yield farming, or trading, allowing you to unlock dual income streams.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Liquid Staking?
The core advantage is liquidity; your staked assets continue earning while remaining fully usable in DeFi. You can use stETH on Aave, trade mSOL on Jupiter, or deposit rETH into
Balancer for additional yield. However, liquid staking adds smart contract risk, platform dependency, and potential depegging, where the LST diverges in value from its underlying asset due to liquidity issues or volatility.
When to Choose Liquid Staking
Liquid staking is best suited for active DeFi users and yield seekers who want capital efficiency without sacrificing staking rewards. It’s ideal if you need flexibility, like using stETH as collateral on Aave or trading mSOL on
Jupiter, while continuing to earn passive income. If you're comfortable with managing protocol risks and navigating DeFi, liquid staking offers the most powerful way to put your crypto to work in 2025.
Final Thoughts: What’s the Best Type of Staking to Choose in 2025?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to staking in 2025. Each method, native staking, pool staking, and liquid staking, offers a unique balance of accessibility, yield potential, and control. The right choice depends on your financial goals, technical comfort level, and how quickly you may need access to your funds.
Native staking is best suited for long-term holders who prioritize network alignment, direct participation, and lower third-party risk, though it requires locking funds and potentially managing validator responsibilities. Pool staking offers a more accessible option for users with smaller holdings, removing the technical barrier but introducing shared risks and limited liquidity. Liquid staking is ideal for active DeFi participants seeking capital efficiency and flexibility, but it carries added risks related to smart contracts, token depegging, and protocol reliability.
Remember: All forms of staking carry some level of risk, whether it’s slashing penalties, validator downtime, smart contract bugs, or token depegging. Always do your due diligence before committing your assets, and choose platforms with a strong track record, transparent governance, and robust security practices.
In the end, the best staking method is the one that aligns with your risk tolerance, liquidity needs, and investment strategy.
Related Reading